Advanced Airway Management for Nursing
Contents:
Laryngeal mask airways can even be used to deliver general anesthesia. These are followed by infraglottic techniques, such as tracheal intubation , and finally surgical techniques. Advanced airway management is a key component in cardiopulmonary resuscitation , anaesthesia , emergency medicine and intensive care medicine.
Online continuing education course,CE, for nurses, respiratory therapists, and health care providers on airway management. Br J Nurs. Sep ;19(16) Airway management for nurses: emergency assessment and care. Higginson R(1), Jones B, Davies K.
The A in the ABC initialism mnemonic , for dealing with critically ill patients, stands for airway management. Many airways are straightforward to manage. However, some can be challenging. Such difficulties can be predicted to some extent; a recent Cochrane systematic review examines the sensitivity and specificity of the various bedside tests commonly used to predict difficulty in airway management. In advanced airway management foreign objects are either removed by suction or with e.
Airway management for nurses:emergency assessment and care.
If removal is not possible surgical methods should be considered. Supraglottic techniques includes the use of supraglottic tubes, such as oropharyngeal and nasopharyngeal airways, and supraglottic devises such as laryngeal masks.
- Advanced Airway Management Course, Guy's Hospital, London | Difficult Airway Society?
- !
- .
- Besides Yourself.
- ;
Common for all supraglottic devises are that they are introduced into the pharynx , ensuring the upper respiratory tract remains open, without passing through the glottis and thereby entering the trachea. Nasopharyngeal airways is a soft rubber or plastic hollow tube that is passed through the nose into the posterior pharynx. Oropharyngeal airways are rigid plastic curved devices, which are inserted through the patients mouth.
First, inserting an ET tube usually requires a great deal of skill and takes a considerable amount of time. Typically this is when a cricothyrotomy would be attempted as mentioned above. Downloads Download data is not yet available. However, you may find that attempting to insert a Combitube is a waste of precious time when transporting the patient to the hospital. A Glidescope utilizes a laryngoscopic blade connected by a cable to a large video screen and requires a slightly different technique than that of a traditional laryngoscope. Although many different types of healthcare providers can take ACLS, only a few i.
It prevents the patients tongue from covering the epiglottis and thereby obstructing the airway. An oropharyngeal airway should only be used in a deeply unresponsive patient because in a responsive patient they can cause vomiting and aspiration by stimulating the gag reflex.
Supraglottic airways or extraglottic devices [6] are a family of devices that are inserted through the mouth to sit on top of the larynx. Supraglottic airways are used in the majority of operations performed under general anaesthesia. The best-known example is the laryngeal mask airway. A laryngeal mask airway is an airway placed into the mouth and set over the glottis and inflated. There are specific indications or guidelines for deciding a more invasive and more secure airway is worth the associated risk [9]:.
Tracheal intubation, often simply referred to as intubation , is the placement of a flexible plastic or rubber tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation , and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction.
The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an endotracheal tube is passed through the mouth and vocal apparatus into the trachea.
In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Classically tracheal intubation has been performed utilizing laryngoscopic blades to obtain direct visualization of the vocal cords. Even in this category there are multiple different blade styles, shapes and lengths from which to choose. Multiple intubation tools are now available with built-in video technology. A Glidescope utilizes a laryngoscopic blade connected by a cable to a large video screen and requires a slightly different technique than that of a traditional laryngoscope.
The McGrath model has a compact design with a smaller screen directly attached to the blade. Studies have shown that video laryngoscopes when compared to classic models resulted in fewer failed intubation attempts, especially in those patients designated as more difficult airways. These devices are quickly finding their way into emergency departments , operating theaters and critical care floors across the world.
Alternatives to standard endotracheal tubes includes laryngeal tube and combitube.
- Advanced airway management.
- Der Roman im Fremdsprachenunterricht (German Edition)!
- Airway management for nurses:emergency assessment and care.;
The absolute gold standard for confirming successful placement of an endotracheal tube is direct visualization of the tube passing through the vocal cords. Other methods used as secondary confirmation include carbon dioxide detectors , capnography , oxygen saturation , chest x-ray , or equal chest rise and equal breath sounds heard on both sides of the chest. Surgical methods for airway management rely on making a surgical incision is made below the glottis in order to achieve direct access to the lower respiratory tract , bypassing the upper respiratory tract.
Surgical airway management is often performed as a last resort in cases where orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation are impossible or contraindicated. Surgical airway management is also used when a person will need a mechanical ventilator for a longer period. Surgical methods for airway management include cricothyrotomy and tracheostomy. A cricothyrotomy is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema , or massive facial trauma.
Bag Valve Mask Superior to Advanced Airways
Cricothyrotomy is easier and quicker to perform than tracheotomy, does not require manipulation of the cervical spine and is associated with fewer complications. A tracheotomy is a surgically created opening from the skin of the neck down to the trachea. It is always important not to think of children as just small adults. They are unique in far more ways than simply being smaller in size. This means that the likelihood of complications related to insertion of the ET tube is much higher. In fact, inserting a tube is often fraught with complications, even for experienced practitioners.
- LEducation dune fée (Litterature) (French Edition);
- Advanced Airways: Best Practices.
- The Frequency Of Murder.
- 300 lustige Namen für deinen Penis - Porno in der eigenen Hose: Wie Männer ihren besten Freund nennen (Illustrierte Ausgabe) (German Edition);
- Nurses and advanced airway management: the experience of the Piacenza ambulance service.
- Éléments de Géométrie Rigide: Volume I. Construction et Étude Géométrique des Espaces Rigides: 286 (Progress in Mathematics) (French Edition).
- Article Sidebar?
However, with the bag valve mask, the airway can be maintained and rescue breaths can be provided effectively. Even in situations where insertion of a tube would not take a great deal of time, it is better to use a bag valve mask if ventilations are being provided effectively to ensure that no complications arise from a misplaced tube. In hospital, the ET tube should be placed by a physician, but even then it should only be attempted if there is no other choice. If the patient begins to breathe spontaneously, an ET tube will not be necessary.
Advanced Airway Management Course, Guy's Hospital, London
In the end, though, only doctors with a great deal of experience, such as anesthesiologists and emergency room physicians, should attempt to insert an ET tube. There are several types of devices, and they all revolve around the subglottal region. This means that they are inserted to or just beyond the back of the throat, but they do not descend into the lungs.
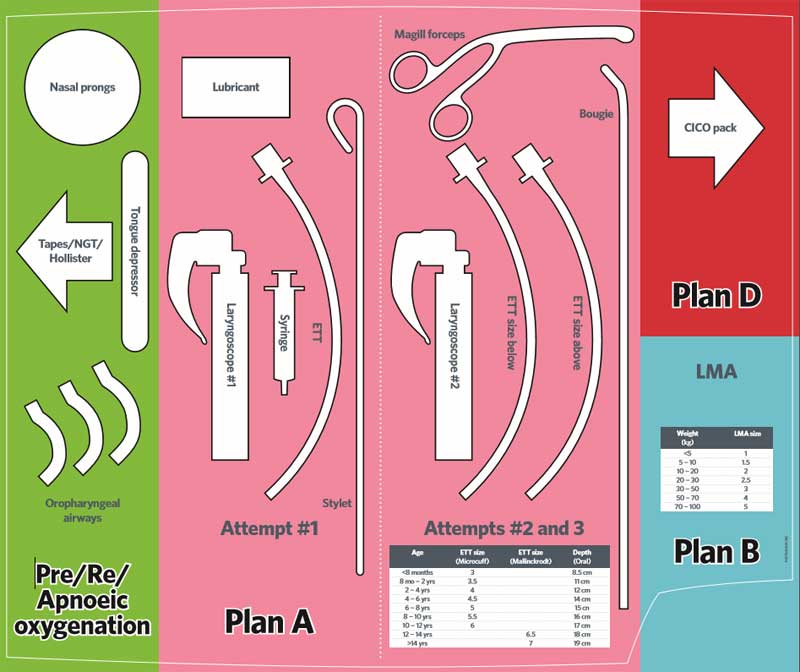
They are easier to place than ET tubes, and they have fewer risks associated with insertion. Again, training with these devices is key. One such device is the Combitube, which blocks off the esophagus and directs air into the trachea. This causes fewer instances of aspiration, more reliable ventilation during ACLS, and mechanical isolation of the airway. However, you may find that attempting to insert a Combitube is a waste of precious time when transporting the patient to the hospital. In the hospital, the doctors there are more likely to intubate, and a Combitube would only be used if intubation with an ET tube was unsuccessful.
Endotracheal intubation is the Everest of emergency procedures. When it is performed by inexperienced practitioners, it can lead to trauma of the oropharynx, intubation of the esophagus, and injury to the lungs themselves. While in hospital, the placement of the tube can be checked by several methods, such as x-ray, but many of these methods of verifying placement are not available in the field. This may mean that you are giving breaths that are not helping the patient and you are, in fact, hurting them.