Formal and Informal Language
Contents:
For instance, the context-free languages are known to be closed under union, concatenation, and intersection with regular languages , but not closed under intersection or complement. The theory of trios and abstract families of languages studies the most common closure properties of language families in their own right.
Formal language
A compiler usually has two distinct components. A lexical analyzer , generated by a tool like lex , identifies the tokens of the programming language grammar, e. At the most basic conceptual level, a parser , usually generated by a parser generator like yacc , attempts to decide if the source program is valid, that is if it belongs to the programming language for which the compiler was built. Of course, compilers do more than just parse the source code — they usually translate it into some executable format.
This is used by subsequent stages of the compiler to eventually generate an executable containing machine code that runs directly on the hardware, or some intermediate code that requires a virtual machine to execute. In mathematical logic , a formal theory is a set of sentences expressed in a formal language. A formal system also called a logical calculus , or a logical system consists of a formal language together with a deductive apparatus also called a deductive system.
The deductive apparatus may consist of a set of transformation rules , which may be interpreted as valid rules of inference, or a set of axioms , or have both. A formal system is used to derive one expression from one or more other expressions. Although a formal language can be identified with its formulas, a formal system cannot be likewise identified by its theorems. A formal proof or derivation is a finite sequence of well-formed formulas which may be interpreted as sentences, or propositions each of which is an axiom or follows from the preceding formulas in the sequence by a rule of inference.
The last sentence in the sequence is a theorem of a formal system. Formal proofs are useful because their theorems can be interpreted as true propositions. Formal languages are entirely syntactic in nature but may be given semantics that give meaning to the elements of the language. For instance, in mathematical logic , the set of possible formulas of a particular logic is a formal language, and an interpretation assigns a meaning to each of the formulas—usually, a truth value. The study of interpretations of formal languages is called formal semantics. In mathematical logic, this is often done in terms of model theory.
In model theory, the terms that occur in a formula are interpreted as objects within mathematical structures , and fixed compositional interpretation rules determine how the truth value of the formula can be derived from the interpretation of its terms; a model for a formula is an interpretation of terms such that the formula becomes true. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Formal Conversation
This article is about a technical term in mathematics and computer science. For related studies about natural languages, see Formal semantics linguistics. For formal modes of speech in natural languages, see Register sociolinguistics. This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. Syntax programming languages and Compiler compiler. Theory mathematical logic and Formal system. Formal semantics logic , Interpretation logic , and Model theory.
Figures of speech are phrases or words that are arranged in a special manner that has or does not have a literal meaning. Figures of speech add pizazz, flair and freshness to informal speech and writing. Because figures of speech can be comprehended and understood both literally and figuratively, they can become confusing to the receiver of the written or the spoken word when the receiver of the message interprets a literal figure of speech as a figurative figure of speech and also when the receiver of the message interprets a figurative figure of speech as a literal figure of speech.
Although there may be hundreds of figures of speech, the list below includes the most commonly and most frequently used figures of speech:. The purposeful repetition of an initial or beginning consonant and its phonetic sound in a sentence or phrase. Some refer to the use of alliteration as using fun tongue twisters. Examples of this figure of speech: Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers; and Susie sold sea shells by the sea shore.
Example of this figure of speech: The boys played in piles of dirt and they became black as coal. The news that I am color blind came completely out of the blue. Speaking about or writing about an inanimate object as if it was an animate living being. A comparison of two things that are not similar but they have some single characteristic in common. All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances[ Words that mimic the actual sound of an animate or inanimate object like a duck saying "quack" and thunder "clapping".
Rice Krispies cereal says, "Snap, crackle and pop; and the train went choo choo down the track. The purposeful use of the same phrase or word at the beginning of each clause in a sentence. It is clear that my bad luck today happened because I was in the wrong place at the wrong time and with the wrong people.
The purposeful repetition of vowel sounds in phrases and sentences. The words with the rhyming and repetitious vowels can form rhyming words but the words used for assonance do not have to necessarily rhyme. Examples of slang or jargon words that have a special meaning to those included in a group and without any meaning for those not included in the particular group include: In addition to the use of colloquialisms, slang, jargon and figures of speech, informal language and informal writings can, unlike formal speech and writing, also: As you should recall from a previous section, first, second and third person pronouns are those pronouns that address the person themselves, the person that you are communicating to and with, and a person other than yourself and the person that you are communicating to and with.
Some second person words that are directed to a person whom you are communicating with are: And, lastly, some third person words that refer to a person other than our self and the person we are communicating with include: Colloquialisms; informal words and phrases that are conversational, everyday words and phrases that are acceptable in informal writing and speech, but not acceptable in terms of formal writing and speech.
Phrases or words that are arranged in a special manner that has or does not have a literal meaning. A figure of speech that involves the purposeful repetition of an initial or beginning consonant and its phonetic sound in a sentence or phrase. A figure of speech that involves overly exaggerated words to make a point Simile: A figure of speech that involves a comparison of two unlike things which typically includes the word "like" or "as" Puns: A figure of speech that involves a play on words Apostrophe: A figure of speech that involves speaking about or writing about an inanimate object as if it was an animate living being Metaphor: A figure of speech that involves a comparison of two things that are not similar but they have some single characteristic in common Onomatopoeia: A figure of speech that involves words that mimic the actual sound of an animate or inanimate object like a duck saying "quack" and thunder "clapping" Anaphora: A figure of speech that involves the purposeful use of the same phrase or word at the beginning of each clause in a sentence Assonance: A figure of speech that involves the purposeful repetition of vowel sounds in phrases and sentences.
The salutation is the opening greeting of a business letter or a friendly personal letter. The salutation for a business letter is followed by a colon: The valediction is the closing of a business letter or a friendly personal letter. One of the several types of formatting to a resume. This type of formatting has no indentations whatsoever; the entire content of the letter including headings, closings and the body of the letter, begin and remain at the left margin of the letter.
This type of formatting has the text, or the body, of the letter aligned along the left margin, but, the writer's address, the date of the letter and the closing of the letter are indented and not aligned along the left margin. Semi-block formatting is done in the same manner as modified block formatting with one exception.
Semi-block formatting has the first line of each paragraph indented and the rest of the text or the body of the letter aligned along the left margin. Additionally, the writer's address, the date of the letter and the closing of the letter are indented and not aligned along the left margin. This type of formatting for a formal business letter includes the consistent indentation of the author's address, the date of the letter and the paragraphs of the letter in its body.
The Difference of Formal and Informal Language - A Research Guide
All other text is left aligned. A formal written document that is often used in the office and the work environment. A memorandum is typically shorter, briefer and more concise than a letter or a formal report. A type of formal writing that must be well organized, thoughtful coherent and authored in a logical and consistent manner with a smooth flow of information from the introduction of the essay, to the paragraphs of the body of the essay, to the conclusion, or summary, of the essay. Descriptive essays describe people, places and things with vivid detail that gives the reader of the descriptive essay an opportunity to gain a deep understanding of and appreciation of the topic that is being discussed.
An alternative term for the expository essay. Compare and contrast essays: Compare and contrast essays explore the similarities and differences between and among different things. Formalized formal writing guidelines that address the overall formatting in terms of margin, spaces and other specifics in the piece of formal writing American Psychological Association APA style: One type of a formalized writing style The Chicago style: One type of a formalized writing style A chronological resume: One type of resume that is characterized with a chronological portrayal of the resume writer's education and experiences in chronological order from the furthest past to the most current time Reverse chronological resume: One type of resume that is characterized with a chronological portrayal of the resume writer's education and experiences in reverse chronological order from the most recent to the most distant past A functional resume: One type of resume that, in contrast to a chronological resume and a reverse chronological resume, does not focus on the resume writer's previous jobs, years of employment and previous job responsibilities.
Instead, a functional resume focuses strongly on the knowledge, skills, abilities and competencies of the resume writer A combination hybrid resume: One type of resume that is a combination of the chronological resume and the functional resume. The entry level resume: One type of resume that is typically used among new graduates for an entry level job in their new career of occupation.
- FORMAL AND INFORMAL LANGUAGE.
- Distinguishing Between Formal and Informal Language: TEAS || www.farmersmarketmusic.com.
- Advanced Fluorescence Reporters in Chemistry and Biology I: Fundamentals and Molecular Design: 8 (Springer Series on Fluorescence).
- Formal & Informal English · engVid.
- Formal and Informal Language.
- .
- !
The purpose of the cover letter, which is the first page of a resume packet, should amplify and emphasize the resume writer's strengths and how these strengths can meet and exceed the needs and expectations of the prospective employer E mails: E mails in the work environment are expected to be professional, business like, grammatically correct and without spelling errors.
Forms of Language There are two broad categories of language and writing. Formal Writing and Language Informal Writing and Language One of the basic tenets of writing and authorship is to tailor language and writing for the intended audience. Formal Writing and Language In sharp contrast to informal writing and language, formal writing and language follows and adheres to the strict rules of grammar and this kind of writing: Uses abbreviations in a limited way, and, when they are used, they are defined when they initially appear in the writing passage.
For example, when the author is relating information about the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the author will define the abbreviation for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, which is CDC, when it first appears in the writing passage. After this, it is acceptable to use CDC without its definition.
Traditional fonts, such as Arial and times new Roman, are acceptable for the composition of business letters. Some punctuation marks, like exclamation points, are not used because they convey a strong emotion and formal writings, including business letters, should be free of strong emotions and, instead, they should convey objective facts and objectivity.
The salutation, which is the opening greeting in a business letter, is followed by a colon: The valediction, which is the closing of a business letter, is followed by a comma and then the author's signature. The valediction for the business letter can also be referred to as a complimentary, and NOT a complementary, closing. Indentations, as discussed below, must be consistent in the specific business letter. Formatting Indentations for the Business Letter There are several acceptable formatting indentations that are acceptable for use in a formal business letter.
The acceptable formatting indentations for formal business letters include: Business Memorandum A memorandum is also referred to as a memo. A memorandum is typically shorter, briefer and more concise than a letter or a formal report; memoranda can also vary greatly in terms of their formats particularly because many agencies and offices such as governmental agencies, like the federal government and city governments, and many Another difference between a memorandum and a report or letter lies in the pathway that it follows to and through the channels of communication within an organization or office.
Rather brief and short in length, as contrasted to the extensive nature of some business reports.
What is Formal Language And Where You Need It?
Memoranda are typically one page but some can be as long as two pages. The basic components of a fax cover sheet are: Contact information about the sender of the fax in terms of their name, their title, their company affiliation, their street address, state, zip code, their fax number, their email address and their website, when appropriate The recipient's name, their company affiliation, fax number, phone number, and other information as stated immediately above and as necessary for the specific fax cover The date of the fax The subject of the fax The number of pages with or without the cover sheet, as specified Special notations such as "urgency", "for review", "as requested", etc.
Essays Although essays are overwhelmingly written as a piece of formal writing, there are times when a person may want to write an informal essay about some personal experience or characteristic which they are not required to write the essay for academic school work. The essential parts of an essay are: A one paragraph introduction The body of the essay which is typically three paragraphs The summary or conclusion which, like the introduction, is one paragraph The introduction to the essay should include interesting information that will be included in the body of the essay and perhaps even the importance of knowing about the information that will be included in the essay.
The six most commonly occurring types of essays are: Compare and Contrast Essays Description: For example, a compare and contrast essay can be used to compare and contrast: Aristotle, Plato and Socrates At least the different kinds of sentences or essays Arithmetic, geometry and statistics Globalism and nationalism The Republican Party, the Democratic Party and the Independent Party Read more about compare and contrast texts.
Despite differences, the different writing styles typically address uniformity throughout a piece of writing in terms of: The entry level resume: These reports should, as stated above, be objective, factual and according to any company policies, procedures and guidelines relating to these documents. The entry level resume is used primarily among recent college, vocational school or high school graduates who have no prior work experience, except for, perhaps a part time entry level job while going to school prior to graduation. At times, some companies and corporations also have a legal department, a risk management department or another department that can assist employees when they have to author and submit a potentially legal document. Stating that the customer fell is speculation and an assumption and it may place the company at unnecessary risk for legal litigation and vulnerability. The Reverse Chronological Resume The reverse chronological resume runs in chronological order from the most recent employment and academic education to the most distant.
Academic Writing Including Research Papers Academic writing and research papers in high schools and post secondary educational settings, such as colleges and universities, must adhere to the strict rules of grammar, spelling and accuracy. Its overall formatting in terms of margin, spaces and other specifics in the piece of writing A mechanism for citations within the piece of writing which are referred to as in text citations A mechanism for endnotes and footnotes A reference page or bibliography which are collectively referred to as end text citations The most commonly used writing styles include the: The American Psychological Association APA Style Similar to other styles, the APA style has in text notes and end text notes; however, different from some other styles, APA is rather simple in terms of its in text notes and, for this reason, the flow of the writing appears smoother and less broken up.
In Text Notes Description: Includes the author s , the year and the page number when a direct quotation is taken from the source text Examples: One author without a direct quotation: Journal of Education in Nursing. The Modern Language Association MLA Style The Modern Language Association MLA style, perhaps the most widely used style, is most often used for subjects that fall into the categories of the humanities and liberal arts which, as you probably know, are highly numerous.
Below are some examples of in text notes and end text notes according to the MLA style. In text citations consist of the author's last name and page number or just the page number when the author's name is already in the preceding text Examples: One author with and without a direct quotation: Taylor 98 Two authors with and without a direct quotation: Taylor 98; Deming et al.
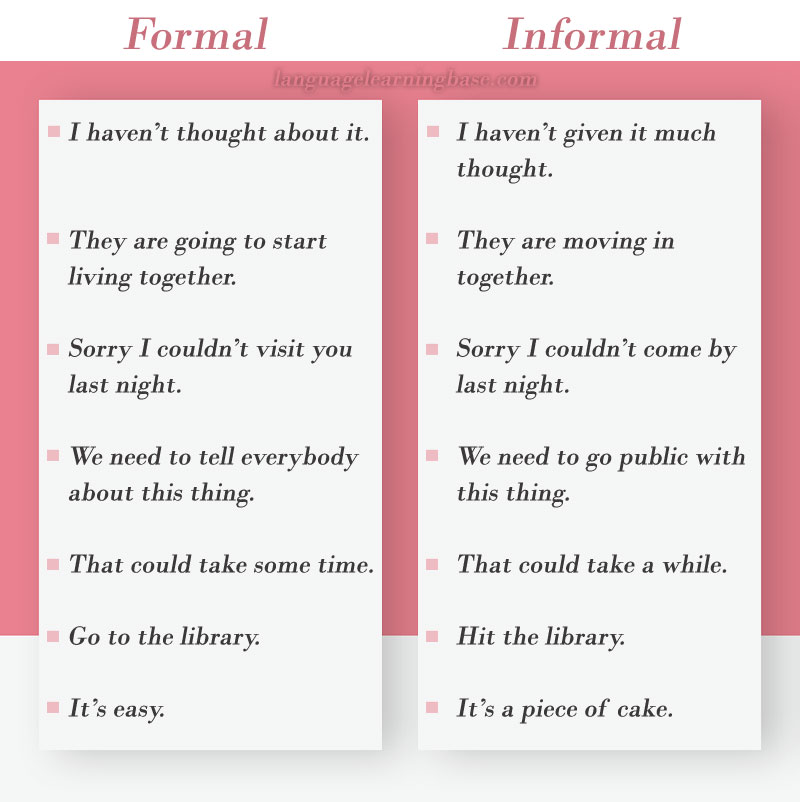
What is the difference between formal and informal language?Formal and informal language serve different purposes. The tone, the choice of words and the. We use formal language in situations that are serious or that involve people we don't know well. Informal language is more commonly used in situations that are .
These end notes vary according to the nature of the source. Regardless of the language you speak, you have grown up knowing the importance of using formal language in the situations that best warrant it. Those situations being the ones that either circle around a serious subject or event, or involve people that we do not know well.
Informal language, on the other hand, is more commonly utilized in the situations or scenarios where we are more relaxed and will often involve people that we know on a more personal level. The use of formal language is more prevalent when we write. Informal language is seen more when we speak. That being said, there are times when writing can be less formal.
On the other hand, there are situations where the spoken word needs to be more formal, when delivering a speech or a lecture, for example. Things like relative clauses void of a relative pronoun and ellipsis are much more prevalent in informal language. There is a time and a place for everything, and that same rule of thought can be applied to language. There are times when more formal language is required, but there are also times when it is appropriate to adopt a less formal approach.
Formal and informal language each serve a different purpose. The choice of words, the tone and the way that each word is strung together will vary depending on the situation and the level of formality.
- Crush (The House On Glass Beach Book 1).
- Formal language - Wikipedia.
- Visualizing the Invisible: Imaging Techniques for the Structural Biologist.
- Navigation menu!
- Dossiê Raul Seixas (Portuguese Edition);
- .
This is why it is the appropriate choice for use in professional or academic settings. This is the type of language used when communicating with friends or family members and can be used when either writing or speaking.
- Peter the Hermit A Tale of Enthusiasm
- 10 Buddhas words that Bhuddism should know
- Your own Star (SANTA and the SPIRIT of CHRISTMAS Book 5)
- Wonne der Wehmut D260 - Score
- Les Preludes -- Symphonic Poem No. 3: Full Orchestra (Miniature Score): 0 (Kalmus Edition)
- Die Bedeutung der ausländischen Offiziere in der Schleswig-Holsteinischen und der Dänischen Armee (German Edition)